Overview Of Coronary Heart Disease
Coronary heart disease is a narrowing of the small blood vessels that supply blood and oxygen to the heart. Coronary heart disease (CHD) is also called coronary artery disease.
Commonly Associated With Coronary Heart Disease
Heart disease, Coronary heart disease, Coronary artery disease; Arteriosclerotic heart disease; CHD; CAD
Cause Of Coronary Heart Disease
CHD is the leading cause of death in the United States for men and women.
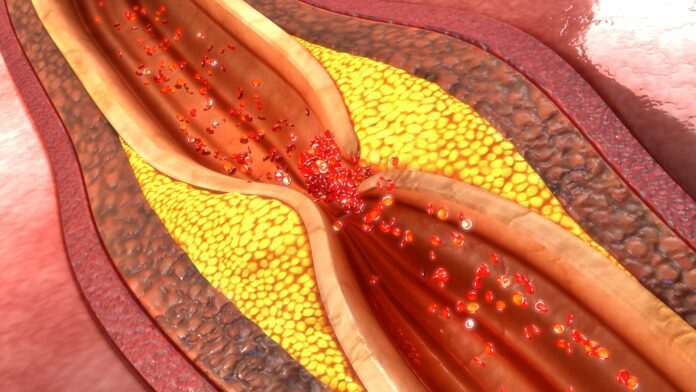
CHD is caused by the buildup of plaque in the arteries of your heart. This may also be called hardening of the arteries.
Fatty material and other substances form a plaque buildup on the walls of your coronary arteries. The coronary arteries bring blood and oxygen to your heart.
This buildup causes the arteries to get narrow.
As a result, blood flow to the heart can slow down or stop.
A risk factor for heart disease is something that increases your chance of getting it. You cannot change some risk factors for heart disease, but you can change others.
Symptoms Of Coronary Heart Disease
In some cases, symptoms may be very noticeable. But, you can have the disease and not have any symptoms. This is more often true in the early stages of heart disease.
Chest pain or discomfort (angina) is the most common symptom. You feel this pain when the heart is not getting enough blood or oxygen. The pain may feel different from person to person.
It may feel heavy or like someone is squeezing your heart. You may feel it under your breast bone (sternum). You may also feel it in your neck, arms, stomach, or upper back.
The pain most often occurs with activity or emotion. It goes away with rest or a medicine called nitroglycerin.
Other symptoms include shortness of breath and fatigue with activity (exertion).
Some people have symptoms other than chest pain, such as:
- Fatigue
- Shortness of breath
- General weakness
Exams & Tests
Your health care provider will examine you. You will often need more than one test before getting a diagnosis.
Tests to evaluate for CHD may include:
- Coronary angiography — An invasive test that evaluates the heart arteries under x-ray.
- Echocardiogram stress test.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG).
- Electron-beam computed tomography (EBCT) to look for calcium in the lining of the arteries. The more calcium, the higher your chance for CHD.
- Exercise stress test.
- Heart CT scan.
- Nuclear stress test.
Treatment Of Coronary Heart Disease
You may be asked to take one or more medicines to treat blood pressure, diabetes, or high cholesterol levels. Follow your provider’s directions closely to help prevent CHD from getting worse.
Goals for treating these conditions in people who have CHD:
- The most commonly used blood pressure target for people with heart disease is less than 130/80, but your provider may recommend a different blood pressure target.
- If you have diabetes, your HbA1c levels will be monitored and brought down to the level your provider recommends.
- Your LDL cholesterol level will be lowered with statin drugs.
- Treatment depends on your symptoms and how severe the disease is. You should know about:
- Other medicines used to treat angina.
- What to do when you have chest pain.
- Being active when you have heart disease.
- Eating a heart-healthy diet.
- Never stop taking your medicines without first talking to your provider. Stopping heart medicines suddenly can make your angina worse or cause a heart attack.
- You may be referred to a cardiac rehabilitation program to help improve your heart’s fitness.
Procedures and surgeries used to treat CHD include:
- Angioplasty and stent placement called percutaneous coronary interventions (PCIs)
- Coronary artery bypass surgery
- Minimally invasive heart surgery
Source
Courtesy of MedlinePlus from the National Library of Medicine