Overview Of Thyroid Disorders
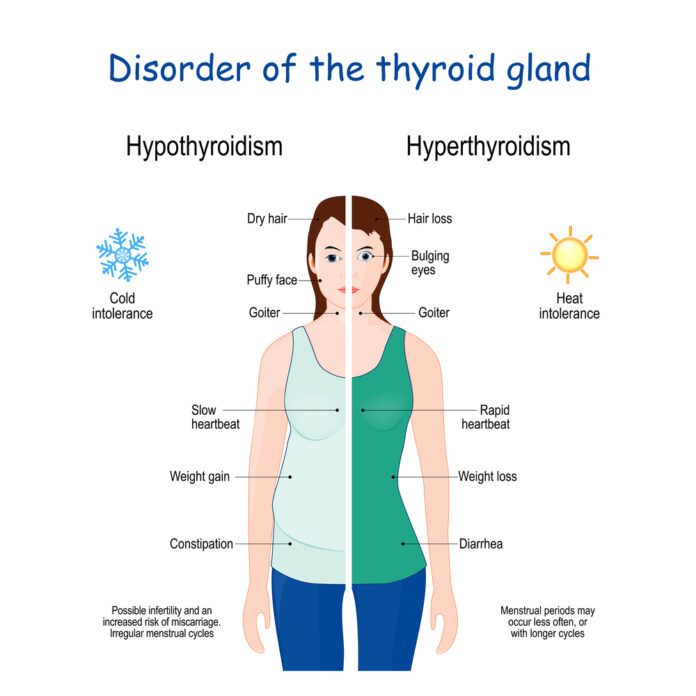
Hypothyroidism, or underactive thyroid, is one of the two main thyroid disorders. This condition occurs when your thyroid gland doesn’t make enough thyroid hormones to meet your body’s needs.
Your thyroid is a small, butterfly-shaped gland in the front of your neck. It makes hormones that control the way the body uses energy. These hormones affect nearly every organ in your body and control many of your body’s most important functions. For example, they affect your breathing, heart rate, weight, digestion, and moods. Without enough thyroid hormones, many of your body’s functions slow down. But there are treatments that can help.
Causes Of Thyroid Disorders
Hypothyroidism has several causes. They include:
- Hashimoto’s disease, an autoimmune disorder where your immune system attacks your thyroid. This is the most common cause.
- Thyroiditis, inflammation of the thyroid
- Congenital hypothyroidism, hypothyroidism that is present at birth
- Surgical removal of part or all of the thyroid
- Radiation treatment of the thyroid
- Certain medicines
- In rare cases, pituitary disease or too much or too little iodine in your diet
Symptoms
The symptoms of hypothyroidism can vary from person to person and may include:
- Fatigue
- Weight gain
- A puffy face
- Trouble tolerating cold
- Joint and muscle pain
- Constipation
- Dry skin
- Dry, thinning hair
- Decreased sweating
- Heavy or irregular menstrual periods
- Fertility problems in women
- Depression
- Slowed heart rate
- Goiter, an enlarged thyroid that may cause your neck to look swollen. Sometimes it can cause trouble with breathing or swallowing.
- Because hypothyroidism develops slowly, many people don’t notice symptoms of the disease for months or even years.
Exams & Tests
To make a diagnosis, your health care provider:
- Will take your medical history, including asking about symptoms
- Will do a physical exam
- May do thyroid tests, such as
- TSH, T3, T4, and thyroid antibody blood tests
- Imaging tests, such as a thyroid scan, ultrasound, or radioactive iodine uptake test. A radioactive iodine uptake test measures how much radioactive iodine your thyroid takes up from your blood after you swallow a small amount of it.
Treatment Of Thyroid Disorders
The treatment for hypothyroidism is medicine to replace the hormone that your own thyroid can no longer make. About 6 to 8 weeks after you start taking the medicine, you will get a blood test to check your thyroid hormone level. Your health care provider will adjust your dose if needed. Each time your dose is adjusted, you’ll have another blood test. Once you find the right dose, you will probably get a blood test in 6 months. After that, you will need the test once a year.
If you take your medicine according to the instructions, you usually should be able to control the hypothyroidism. You should never stop taking your medicine without talking with your health care provider first.
If you have Hashimoto’s disease or other types of autoimmune thyroid disorders, you may be sensitive to harmful side effects from iodine. Talk to your health care provider about which foods, supplements, and medicines you need to avoid.
Women need more iodine when they are pregnant because the baby gets iodine from the mother’s diet. If you are pregnant, talk with your health care provider about how much iodine you need.