Overview Of Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is a lifelong (chronic) disease in which there is a high level of sugar (glucose) in the blood. Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes.
Commonly Associated With
Noninsulin-dependent Diabetes; Diabetes – type II; Adult-onset diabetes; Diabetic – type 2 diabetes; Oral hypoglycemic – type 2 diabetes; High blood sugar – type 2 diabetes
Causes Of Type 2 Diabetes
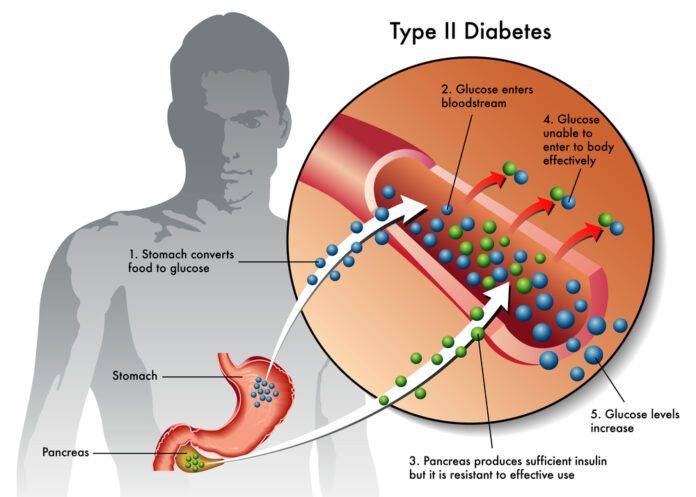
Insulin is a hormone produced in the pancreas by special cells, called beta cells. The pancreas is below and behind the stomach. Insulin is needed to move blood sugar (glucose) into cells. Inside the cells, glucose is stored and later used for energy.
When you have type 2 diabetes, your fat, liver, and muscle cells do not respond correctly to insulin. This is called insulin resistance. As a result, blood sugar does not get into these cells to be stored for energy.
When sugar cannot enter cells, a high level of sugar builds up in the blood. This is called hyperglycemia. The body is unable to use glucose for energy. This leads to the symptoms of type 2 diabetes.
Type 2 diabetes usually develops slowly over time. Most people with the disease are overweight or obese when they are diagnosed. Increased fat makes it harder for your body to use insulin the correct way.
Type 2 diabetes can also develop in people who are not overweight or obese. This is more common in older adults.
Family history and genes play a role in type 2 diabetes. Low activity level, poor diet, and excess body weight around the waist increase your chance of getting the disease.
Symptoms Of Type 2 Diabetes
People with type 2 diabetes often have no symptoms at first. They may not have symptoms for many years.
Early symptoms of diabetes caused by a high blood sugar level may include:
- Bladder, kidney, skin, or other infections that are more frequent or heal slowly
- Fatigue
- Hunger
- Increased thirst
- Increased urination
- Blurred vision
- After many years, diabetes can lead to serious health problems, and as a result, many other symptoms.
Exams & Tests
Your health care provider may suspect that you have diabetes if your blood sugar level is higher than 200 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) or 11.1 mmol/L.
To confirm the diagnosis, one or more of the following tests must be done.
- Fasting blood glucose level — Diabetes is diagnosed if it is 126 mg/dL (7.0 mmol/L) or higher two different times.
- Hemoglobin A1c (A1C) test — Diabetes is diagnosed if the test result is 6.5% or higher.
- Oral glucose tolerance test — Diabetes is diagnosed if the glucose level is 200 mg/dL (11.1 mmol/L) or higher 2 hours after drinking a special sugar drink.
Diabetes screening is recommended for:
- Overweight children who have other risk factors for diabetes, starting at age 10 and repeated every 2 years
- Overweight adults (BMI of 25 or higher) who have other risk factors, such as high blood pressure, or having a mother, father, sister, or brother with diabetes
- Overweight women who have other risk factors, such as high blood pressure, who are planning to become pregnant
- Adults starting at age 45 every 3 years, or at a younger age if the person has risk factors
- If you have been diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, you need to work closely with your provider. See your provider as often as instructed. This may be every 3 months.
The following exams and tests will help you and your provider monitor your diabetes and prevent problems.
- Check the skin, nerves, and joints of your feet and legs.
- Check if your feet are getting numb (diabetic nerve disease).
- Have your blood pressure checked at least once a year (blood pressure goal should be 140/80 mm Hg or lower).
- Have your A1C tested every 6 months if your diabetes is well controlled. Have the test every 3 months if your diabetes is not well controlled.
- Have your cholesterol and triglyceride levels checked once a year.
- Get tests at least once a year to make sure your kidneys are working well (microalbuminuria and serum creatinine).
- Visit your eye doctor at least once a year, or more often if you have signs of diabetic eye disease.
- See the dentist every 6 months for a thorough dental cleaning and exam. Make sure your dentist and hygienist know that you have diabetes.
- Your provider may want to check your vitamin B12 blood levels if you are taking the drug metformin.
Treatment Of Type 2 Diabetes
At first, the goal of treatment is to lower your high blood glucose level. The long-term goals are to prevent complications. These are health problems that can result from having diabetes.
The most important way to treat and manage type 2 diabetes is by being active and eating healthy foods.
Everyone with diabetes should receive proper education and support about the best ways to manage their diabetes. Ask your provider about seeing certified diabetes care and education specialist and a dietitian.
LEARN THESE SKILLS
Learning diabetes management skills will help you live well with diabetes. These skills help prevent health problems and the need for medical care.
Skills include:
- How to test and record your blood glucose
- What, when, and how much to eat
- How to safely increase your activity and control your weight
- How to take medicines, if needed
- How to recognize and treat low and high blood sugar
- How to handle sick days
- Where to buy diabetes supplies and how to store them
- It may take several months to learn these skills. Keep learning about diabetes, its complications, and how to control and live well with the disease. Stay up-to-date on new research and treatments. Make sure you are getting information from trustworthy sources, such as your provider and diabetes educator.
MANAGING YOUR BLOOD SUGAR
Checking your blood sugar level yourself and writing down the results tells you how well you are managing your diabetes. Talk to your provider and diabetes educator about how often to check.
To check your blood sugar level, you use a device called a glucose meter. Usually, you prick your finger with a small needle, called a lancet. This gives you a tiny drop of blood. You place the blood on a test strip and put the strip into the meter. The meter gives you a reading that tells you the level of your blood sugar.
Your provider or diabetes educator will help set up a testing schedule for you. Your provider will help you set a target range for your blood sugar numbers.
Keep these factors in mind:
- Most people with type 2 diabetes only need to check their blood sugar once or twice a day.
- If your blood sugar level is under control, you may only need to check it a few times a week.
- You may test yourself when you wake up, before meals, and at bedtime.
- You may need to test more often when you are sick or under stress.
- You may need to test more often if you are having more frequent low blood sugar symptoms.
- Keep a record of your blood sugar for yourself and your provider. Based on your numbers, you may need to make changes to your meals, activity, or medicines to keep your blood sugar level in the right range. Always bring your blood glucose meter to medical appointments so the data can be downloaded and discussed.
Your provider may recommend that you use a continuous glucose monitor (CGM) to measure blood sugar if:
- You are using insulin injections many times a day
- You have had an episode of severe low blood sugar
- Your blood sugar level varies a lot
- The CGM has a sensor that is inserted just under the skin to measure glucose in your tissue fluid every 5 minutes.
HEALTHY EATING AND WEIGHT CONTROL
Work closely with your health care providers to learn how much fat, protein, and carbohydrates you need in your diet. Your meal plans should fit your lifestyle and habits and should include foods that you like.
Managing your weight and having a well-balanced diet are important. Some people with type 2 diabetes can stop taking medicines after losing weight. This does not mean that their diabetes is cured. They still have diabetes.
Obese people whose diabetes is not well managed with diet and medicine may consider weight loss (bariatric) surgery.
REGULAR PHYSICAL ACTIVITY
Regular activity is important for everyone. It is even more important when you have diabetes. Exercise is good for your health because it:
- Lowers your blood sugar level without medicine
- Burns extra calories and fat to help manage your weight
- Improves blood flow and blood pressure
- Increases your energy level
- Improves your ability to handle stress
- Talk to your provider before starting any exercise program. People with type 2 diabetes may need to take special steps before, during, and after physical activity or exercise, including adjusting doses of insulin if needed.
MEDICINES TO TREAT DIABETES
If diet and exercise do not help keep your blood sugar at normal or near-normal levels, your provider may prescribe medicine. Since these drugs help lower your blood sugar level in different ways, your provider may have you take more than one drug.
Some of the most common types of medicines are listed below. They are taken by mouth or injection.
- Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors
- Biguanides
- Bile acid sequestrants
- DPP-4 inhibitors
- Injectable medicines (GLP-1 analogs)
- Meglitinides
- SGLT2 inhibitors
- Sulfonylureas
- Thiazolidinediones
You may need to take insulin if your blood sugar cannot be controlled with some of the above medicines. Most commonly, insulin is injected under the skin using a syringe, insulin pen, or pump. Another form of insulin is the inhaled type. Insulin cannot be taken by mouth because the acid in the stomach destroys the insulin.
PREVENTING COMPLICATIONS
Your provider may prescribe medicines or other treatments to reduce your chance of developing some of the more common complications of diabetes, including:
- Eye disease
- Kidney disease
- Heart disease and stroke
- FOOT CARE
People with diabetes are more likely than those without diabetes to have foot problems. Diabetes damages the nerves. This can make your feet less able to feel pressure, pain, heat, or cold. You may not notice a foot injury until you have severe damage to the skin and tissue below, or you get a severe infection.
Diabetes can also damage blood vessels. Small sores or breaks in the skin may become deeper skin sores (ulcers). The affected limb may need to be amputated if these skin ulcers do not heal or become larger, deeper, or infected.
To prevent problems with your feet:
- Stop smoking if you smoke.
- Improve control of your blood sugar.
- Get a foot exam by your provider at least twice a year to learn if you have nerve damage.
- Ask your provider to check your feet for problems such as calluses, bunions or hammertoes. These need to be treated to prevent skin breakdown and ulcers.
- Check and care for your feet every day. This is very important when you already have nerve or blood vessel damage or foot problems.
- Treat minor infections, such as athlete’s foot, right away.
- Use moisturizing lotion on dry skin.
- Make sure you wear the right kind of shoes. Ask your provider what type of shoe is right for you.
EMOTIONAL HEALTH
Living with diabetes can be stressful. You may feel overwhelmed by everything you need to do to manage your diabetes. But taking care of your emotional health is just as important as your physical health.
Ways to relieve stress include:
- Listening to relaxing music
- Meditating to take your mind off your worries
- Deep breathing to help relieve physical tension
- Doing yoga, taichi, or progressive relaxation
- Feeling sad or down (depressed) or anxious sometimes is normal. But if you have these feelings often and they’re getting in the way of managing your diabetes, talk with your health care team. They can find ways to help you feel better.
People with diabetes should make sure to keep up on their vaccination schedule.