Overview Of Hemophilia B
Hemophilia B is a hereditary bleeding disorder caused by a lack of blood clotting factor IX. Without enough factor IX, the blood cannot clot properly to control bleeding.
Commonly Associated With
Christmas disease; Factor IX hemophilia; Bleeding disorder – hemophilia B
Causes Of Hemophilia B
When you bleed, a series of reactions take place in the body that helps blood clots form. This process is called the coagulation cascade. It involves special proteins called coagulation, or clotting factors. You may have a higher chance of excess bleeding if one or more of these factors are missing or are not functioning as they should.
Factor IX (nine) is one such coagulation factor. Hemophilia B is the result of the body not making enough factor IX. Hemophilia B is caused by an inherited X-linked recessive trait, with the defective gene located on the X chromosome.
Females have two copies of the X chromosome. If the factor IX gene on one chromosome does not work, the gene on the other chromosome can do the job of making enough factor IX.
Males have only one X chromosome. If the factor IX gene is missing on a boy’s X chromosome, he will have Hemophilia B. For this reason, most people with hemophilia B are male.
If a woman has a defective factor IX gene, she is considered a carrier. This means the defective gene can be passed down to her children. Boys born to such women have a 50% chance of having hemophilia B. Their daughters have a 50% chance of being a carrier.
All female children of men with hemophilia carry the defective gene.
Risk factors for hemophilia B include:
- Family history of bleeding
- Being male
Symptoms Of Hemophilia B
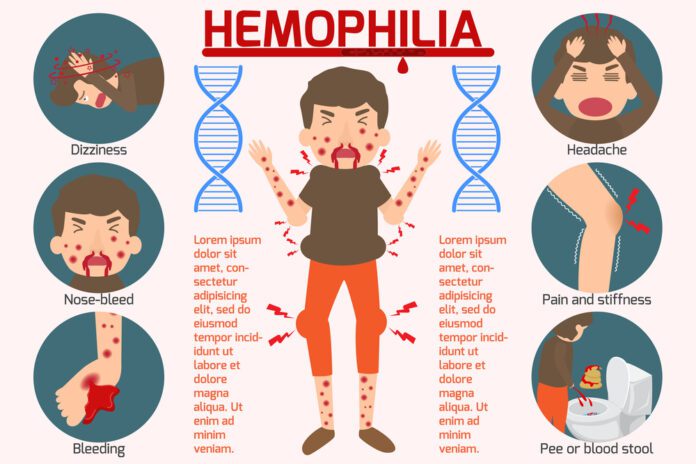
Severity of symptoms can vary. Prolonged bleeding is the main symptom. It is often first seen when the infant is circumcised. Other bleeding problems usually show up when the infant starts crawling and walking.
Mild cases may go unnoticed until later in life. Symptoms may first occur after surgery or injury. Internal bleeding may occur anywhere.
Symptoms may include:
- Bleeding into joints with associated pain and swelling
- Blood in the urine or stool
- Bruising
- Gastrointestinal tract and urinary tract bleeding
- Nosebleeds
- Prolonged bleeding from cuts, tooth extraction, and surgery
- Bleeding that starts without cause
Exams & Tests
If you are the first person in the family to have a suspected bleeding disorder, your health care provider will order a series of tests called a coagulation study. Once the specific defect has been identified, other people in your family will need tests to diagnose the disorder.
Tests to diagnose hemophilia B include:
- Partial thromboplastin time (PTT)
- Prothrombin time
- Bleeding time
- Fibrinogen level
- Serum factor IX activity
Treatment Of Hemophilia B
Treatment includes replacing the missing clotting factor. You will receive factor IX concentrates.
How much you get depends on:
- Severity of bleeding
- Site of bleeding
- Your weight and height
- To prevent a bleeding crisis, people with hemophilia and their families can be taught to give factor IX concentrates at home at the first signs of bleeding. People with severe forms of the disease may need regular, preventive infusions.
- If you have severe hemophilia, you may also need to take factor IX concentrate before surgery or certain types of dental work.
- You should get the hepatitis B vaccine. People with hemophilia are more likely to get hepatitis B because they may receive blood products.
- Some people with hemophilia B develop antibodies to factor IX. These antibodies are called inhibitors. The inhibitors attack factor IX so that it no longer works. In such cases, a man-made clotting factor called VIIa can be given.