Overview Of Scabies
Scabies is an easily spread skin disease caused by a very small mite.
Commonly Associated With
Human scabies; Sarcoptes scabiei
Causes Of Scabies
- Scabies is found among people of all groups and ages around the world.
- The disease is spread by skin-to-skin contact with another infected person.
- It is easily spread among people who are in close contact. Whole families are often affected.
- Outbreaks of scabies are more common in nursing homes, nursing facilities, college dorms, and child care centers.
- The mites that cause this condition burrow into the skin and lay their eggs. This forms a burrow that looks like a pencil mark. Eggs hatch in 21 days. The itchy rash is an allergic response to the mite.
- Pets and animals usually do not spread mites which affect humans. It is also very unlikely for scabies to be spread through swimming pools. It is difficult to spread through clothing or bed linen.
- A type of scabies called crusted (Norwegian) scabies is a severe infestation with very large numbers of mites. People whose immune systems are weakened are most affected.
Symptoms Of Scabies
Symptoms of scabies include:
- Severe itching, most often at night.
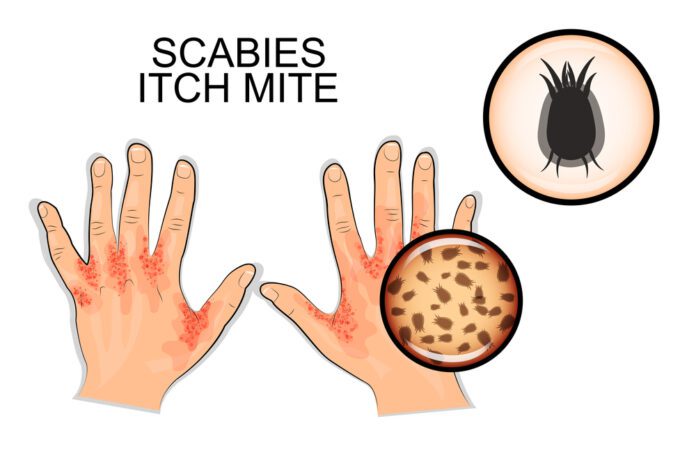
- Rashes, often between the fingers and toes, undersides of the wrists, arm pits, women’s breasts, and buttocks.
- Sores on the skin from scratching and digging.
- Thin lines (burrow marks) on the skin.
- Babies will likely have a rash all over the body, especially on the head, face, and neck, with sores on the palms and soles.
- Scabies doesn’t affect the face except in babies and in people with crusted scabies.
Exams & Tests
The health care provider will examine the skin for signs of scabies.
Tests that may done include:
- Scraping the skin burrows to remove mites, eggs, or mite feces to examine under the microscope.
- In some cases, a skin biopsy is done.
Treatment Of Scabies
HOME CARE
- Before treatment, wash clothes and underwear, towels, bedding, and sleepwear in hot water and dry at 140°F (60°C) or higher. Dry cleaning also works. If washing or dry cleaning can’t be done, keep these items away from the body for at least 72 hours. Away from the body, the mites will die.
- Vacuum carpets and upholstered furniture.
- Use calamine lotion and soak in a cool bath to ease itching.
- Take an oral antihistamine if your provider recommends it for very bad itching.
MEDICINES FROM YOUR HEALTH CARE PROVIDER
- The whole family or sexual partners of infected people should be treated, even if they do not have symptoms.
- Creams prescribed by your provider are needed to treat scabies.
- The cream most often used is permethrin 5%.
- Other creams include benzyl benzoate, sulfur in petrolatum, and crotamiton.
- Apply the medicine all over your body. Creams may be used as a one-time treatment or they may be repeated in 1 week.
- For hard-to-treat cases, the provider may also prescribe a pill known as ivermectin as a one-time dose.